How-to: Metaprogramming
You may often need to write "similar" code for certain cases. The META statement exists for this purpose, and makes it possible to create a code template or metacode. It can contain parameters that will be replaced by certain values when this metacode is used. Such an approach is called metaprogramming.
Let's create a simple directory as described in the article. How-to: CRUD.
CLASS Book 'Book';
name 'Name' = DATA ISTRING[30] (Book) IN id;
FORM book 'Book' // form for displaying "card' // form for displaying the book card
OBJECTS b = Book PANEL
PROPERTIES(b) name
EDIT Book OBJECT b
;
FORM books 'Books'
OBJECTS b = Book
PROPERTIES(b) READONLY name
PROPERTIES(b) NEWSESSION NEW, EDIT, DELETE
LIST Book OBJECT b
;
NAVIGATOR {
NEW books;
}
We can use this code to write the following metacode:
META defineObject(class, id, shortId, caption, multiCaption)
CLASS class caption;
TABLE id(class);
name 'Name' = DATA ISTRING[100] (class);
FORM id caption
OBJECTS shortId = class PANEL
PROPERTIES(shortId) name
EDIT class OBJECT shortId
;
FORM id##s multiCaption
OBJECTS shortId = class
PROPERTIES(shortId) READONLY name
PROPERTIES(shortId) NEWSESSION NEW, EDIT, DELETE
LIST class OBJECT shortId
;
NAVIGATOR {
NEW id##s;
}
END
META defineObject(id, shortId, caption, multiCaption)
@defineObject(###id, id, shortId, caption, multiCaption);
END
Note that one code segment can programmatically call another one.
This is how metacode is used:
@defineObject(book, b, 'Book', 'Books');
@defineObject(magazine, m, 'Magazine', 'Magazines');
In the first case, when the system starts generating the result code, it will replace all id lexemes with book, shortId with b, caption with 'Book', and multiCaption with 'Books'. When using ## concatenation, these replacements will leave everything unchanged. If ### concatenation is used, the first letter of the value will be capitalized. The generated code will look like this:
CLASS Book 'Book';
TABLE book(Book);
name 'Name' = DATA ISTRING[100] (Book);
FORM book 'Book'
OBJECTS b = Book PANEL
PROPERTIES(b) name
EDIT Book OBJECT b
;
FORM books 'Books'
OBJECTS b = Book
PROPERTIES(b) READONLY name
PROPERTIES(b) NEWSESSION NEW, EDIT, DELETE
LIST Book OBJECT b
;
NAVIGATOR {
NEW books;
}
CLASS Magazine 'Magazine';
TABLE magazine(Magazine);
name 'Name' = DATA ISTRING[100] (Magazine);
FORM magazine 'Magazine'
OBJECTS m = Magazine PANEL
PROPERTIES(m) name
EDIT Magazine OBJECT m
;
FORM magazines 'Magazines'
OBJECTS m = Magazine
PROPERTIES(m) READONLY name
PROPERTIES(m) NEWSESSION NEW, EDIT, DELETE
LIST Magazine OBJECT m
;
NAVIGATOR {
NEW magazines;
}
In order for the IDE to "see" the code generated by metacodes, you need to enabled the corresponding mode in the menu.
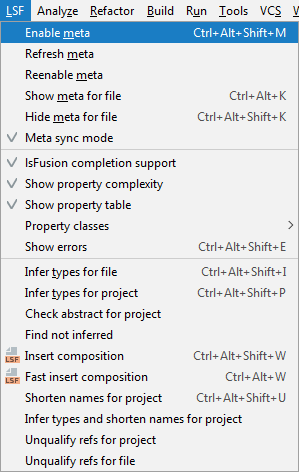
When the metacode support mode is enabled, the generated code will be automatically substituted in the source code if metacode is used.
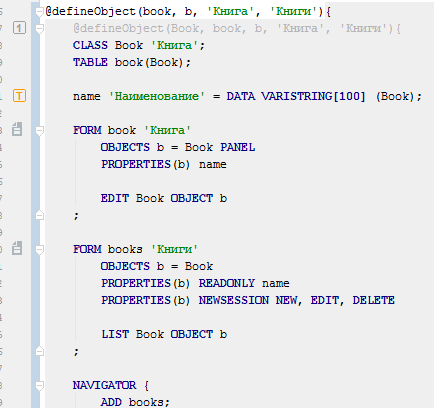
Any modifications of the code will be impossible, since they will be automatically overwritten by the IDE. However, it is recommended to disable this mode when committing code to your version control system to avoid creating redundant change history entries.
Objects created using metacode can subsequently be extended using standard mechanisms.
genre 'Genre' = DATA ISTRING[20] (Book);
EXTEND FORM book PROPERTIES(b) genre;
EXTEND FORM books PROPERTIES(b) genre;